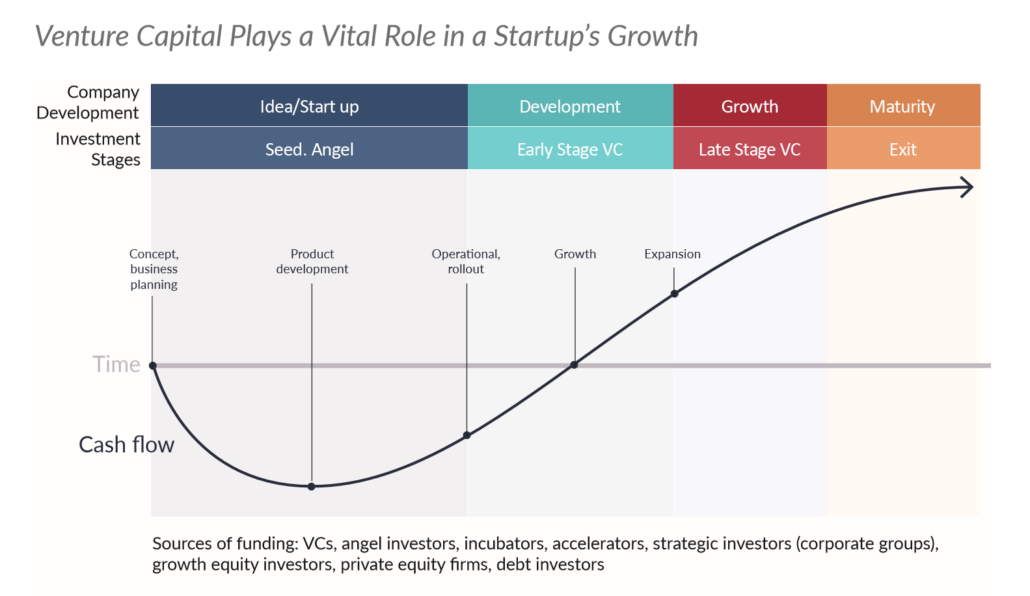
# Venture Capital
## VC Firm
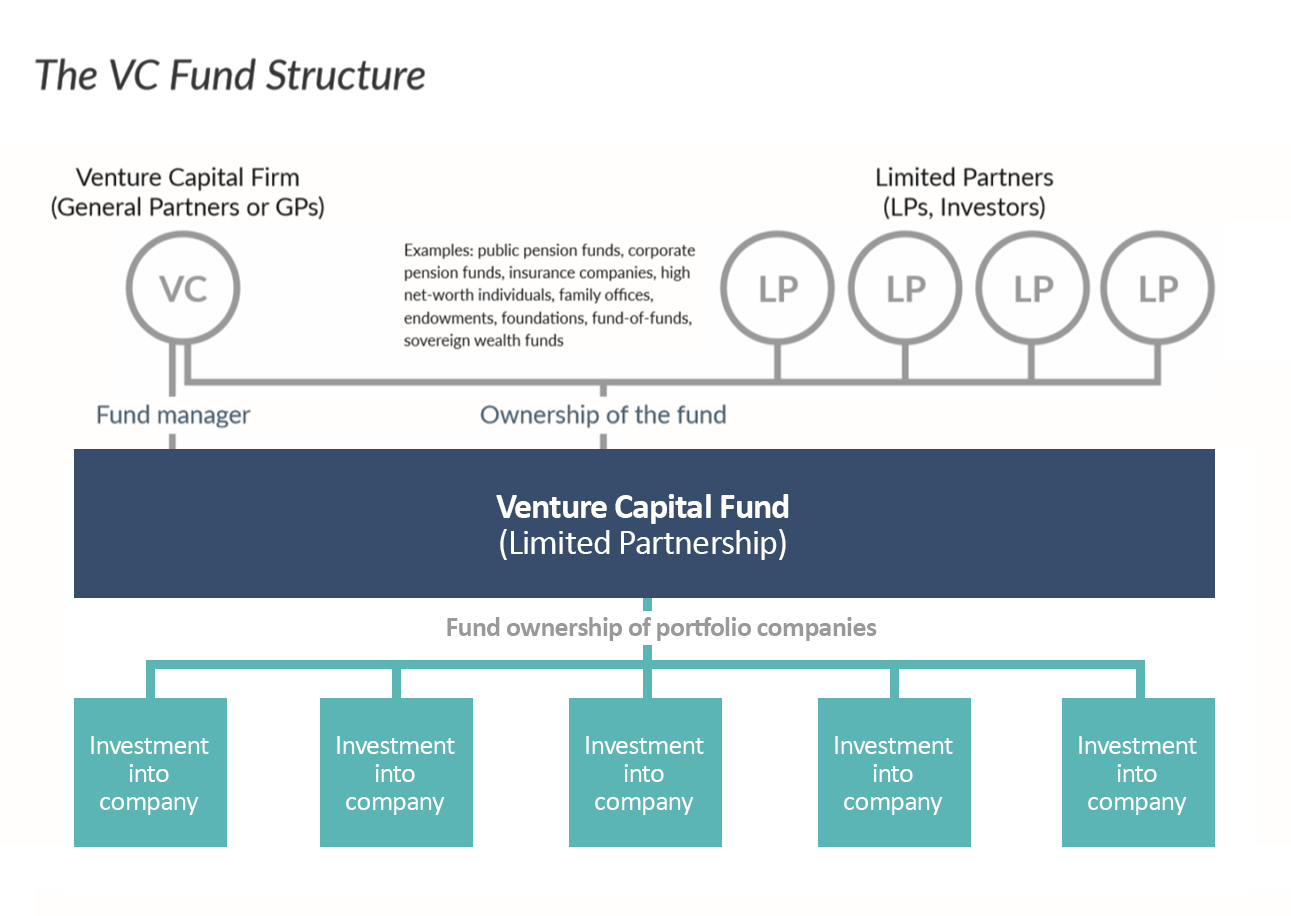
- Venture Capital Firm
- Varies between countries
- Invest in a _venture capital fund_
- About 1k VC firms in the US.
- Very difficult for those without a proven track record as entrepreneur or
investor to form a VC form.
- Two-thirds of the VC firms only launched one fund.
- Venture capital prefers CSE, prefers software even more.
- VC prefers 2B businesses.
- _General Partners_
- Decides the industry to invest in
- Normally 5 to 8 GPs, could be 1
- Arguments: should carried interest be subject to ordinary income or long
term capital gain?
- VC Firm and GPs seek to raise a fund.
- May also put money in.
- Receives _annual fee_, typically 2% of the value of the fund.
- Also receives _carry_, a percentage of net profit (typically 20%)
- Originates from sailing: you pay 20% commission for whatever carried in the
ship.
- Spend half of their time recruiting management and serving as
directors/monitors.
- _Limited Partners_
- Put money into the pool of fund.
- Must wait for 10 to 12 years to see the return.
## The Profit
- Aims for 25% to 35% of profit yearly over the life time of the VC fund.
- A small number of VC funds generates the biggest return (multiple times)
- Vast majority of return is generated by a few successful companies
- Even the best VC firms, they lose money in 40% of the investments.
- Every investment must have the potential to be the home run!
> [!tip] Picking the Winners
>
> - Ideas are more malleable than people.
> - Large addressable market size.
> - Look for startups that grow exponentially without diminishing the marginal
> costs.
> - Look for _unfair_ product, [[business-model|business model]], and culture.
> [!tip] 5 Essential Elements that Lead to Success
>
> - Ideas
> - Team
> - Business Model
> - Funding
> - Timing (most importatn)
## The Process
- VC Firm & GP seek to raise a fund
- GP selects startups
- GP manages fund and more investments over fund life
- GP manages [[ipo|IPO]] or purchase "exits"
- Money were distributed among GP, LP, and other investors.
[Limited Partnership: What It Is, Pros and Cons, How to Form One](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/l/limitedpartnership.asp)
## From Founder and Early Team Point of View
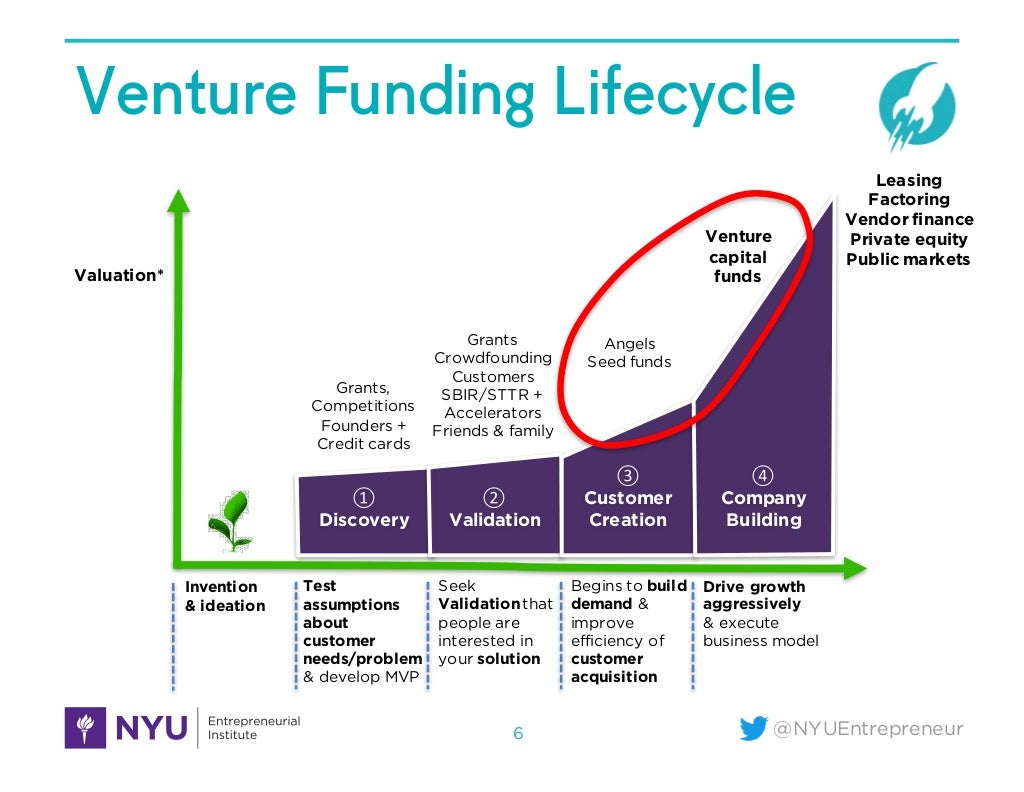
- Venture Funding Lifecycle
- Discovery - Grants, Competition, Credit Cards
- Validation - Crowd Sourcing, SBT, SBI
- Customer Creation - Angels, Seed Funds
- Company Building - Venture Capital
- Founder equity splits
- [Founders' Agreement Template](https://www.pandadoc.com/founders-agreement-template/)
- one-year cliff, four-year vesting
- Founder's Agreement
- [[cap-table|Capitalization Table]]
- [[mvp|Minimum Viable Product (= MVP)]]
- [[stock-option|Stock Options]]
- Incentive
- Non-statutory
## Resources
- [5 charts: Startups feel the squeeze in Q3 | PitchBook | 2023](https://pitchbook.com/news/articles/venture-monitor-charts-startup-exits?)
- "The ratio of capital demand to supply has skyrocketed to its highest level
in over a decade for later-stage startups."
- IPO freeze, investors leaving the VC field, leading to a investors' market
for VC funding.
## Positions
- [[vc-analyst|VC Analyst]]